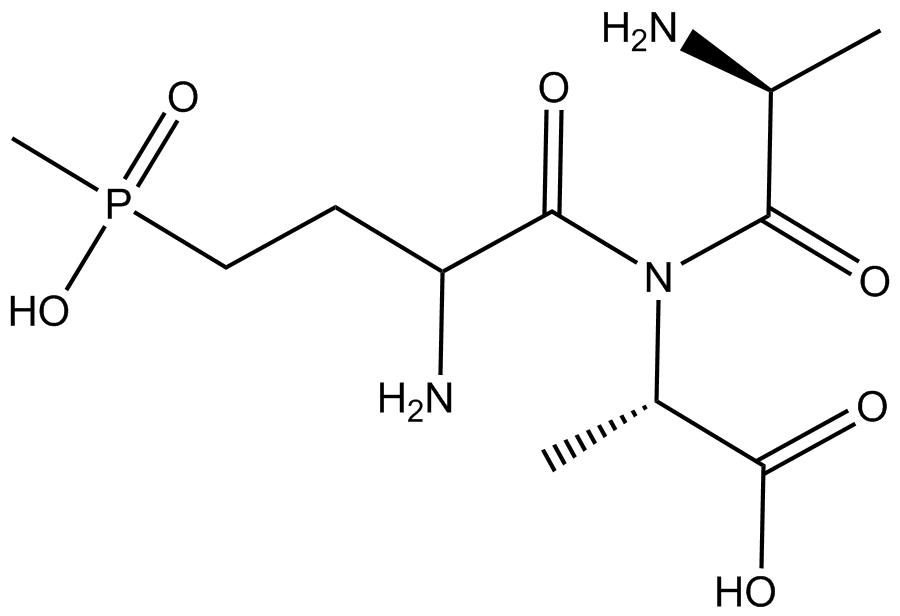
Introduction
Description: Bialaphos is a tripeptide antibiotic with herbicidal properties that is employed in plant transformation for selection of cells containing either the bar or the pat gene.
See product info sheet for more information.
Synonyms: SF-1293, Bilanafos
| Solubility |
Water |
| Physical Form |
Solid |
| Storage Temp. |
-20 °C |
| UPC / SKU |
B131 |
| CAS NUMBER |
71048-99-2 |
| Formula Weight |
345.26 |
| Formula |
C11H21N3NaO6P |
| Synonyms |
SF-1293, Bilanafos |
| Storage Temp. |
-20 °C |
| Tariff Code |
2941.90.6000 |
| Risk Info (R) |
20/21/22 |
| Safety Info (S) |
22-24/25-36/37/39 |
No information available
B131 Bialaphos
| Synonym: |
Bialaphos Sodium Salt, Bilanafos, Phosphinothricin Tripeptide (PTT), SF-1293 |
| CAS: |
71048-99-2 |
| Formula: |
C11H21N3NaO6P |
| Molecular Wt: |
345.27 |
| Properties |
|---|
| Form: |
Powder |
| Appearance: |
Yellow to Orange |
| Application: |
Antibiotic, Selection Agent, Plant Growth Regulator |
| Solubility: |
Soluble in Water |
| Typical Working Concentration: |
Generally 1-3mg/L for selection media,10 mg/L and higher concentrations maybe usedbut results are highly dependent upon plant tissue type. Optimal concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
| Storage Temp: |
-20-0 ºC |
| Storage Temp of Stock Solution: |
-20-0 ºC |
Application Notes
Bialaphos is a
tripeptide antibiotic
with herbicidal properties
that is employed in transformation
research in
many
plant
species that
contain the
bar
gene for selection
purposes.
Bialaphos has
plant growth regulating properties at low concentrations and herbicidal propert
ies
at high concentrations. It wa
s isolated from
Streptomyces
viridochromogenes
(Kumada et al.,
1988)
and inhibits the function
of the enzyme glutamine synthetase (GS)
(Schwartz et al., 2005)
.
Inhibition of GS leads to ammonia build up in plant cells and eventually death unless the
bar
or
pat
gene is present to confer resistance to bialaphos
(Charudattan et al., 1996).
After
biala
phos is taken
into cells, it is
converted into
phosphinothricin
through
hydrolysis
via the
phosphinothricin acetyl transferase enzyme
(Thompson et al., 1987).
References
Arulselvi I, P.Michael, S. Umamaheswari and S. Krishnaveni (2010) Agrobacterium medi
ated
Transformation of
S
orghum
bicolor for disease resistance.
International Journal of
Pharma and Bio Sciences. 1:4.
Casas A.M., Andrzej K. Kononowicz, Usha B. Zehr, Dwight T. Tomes, John D. Axtell, Larry G.
Butler, Ray A. Bressan and Paul M. Hasegawa (19
93)
T
ransgenic
S
orghum plants
v
ia
microprojectile bombardment.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
.
90
:
23,
P
p. 11212
-
11216.
Charudattan R., V. J. Prange, J. T. Devalerio (1996) Exploration of the use of the "bia
laphos
genes" for improving bioherbicide efficacy.
Weed Technology
, 10:3.
D
e Block
M
, J.Botterman, M.Vandewiele, J.Dockx,
C.T
hoen, V.Gossele, N.Rao Movva,
C.Thompson
,
M.Van Montagu and J.Leemans
(1987)
Engineering herbicide resistance in
plants by express
ion of a
detoxifying enzyme
.
The EMBO Journal
6:9 pp.2513
-
2518.
Merck 13, 7425.
Grootbroom AW, NL Mkhonza, MM O'Kennedy, E Chakauya, K Kunert and RK Chikwamba
(2010) Biolistic Mediated Sorghum (
Sorghum
bicolor L. Moench) Transfor
mation v
ia
Mannose and Biala
phose Based Selection Systems.
Internation
al
Journal of Botany
,
6
(2): 89
-
94.
Jube S. and Dulal Borthakur (2007) Expression of bacterial genes in transgenic tobacco:
methods, applications and future prospects.
Electron J Biotechnol
. 10(3): 452
-
467.
Kamo K
And Joyce Van Eck (1997) Effect of bialaphos and phosphinothricin on plant
regeneration from long
-
and short
-
term callus cultures of gladiolus.
In Vitro Cell. Dev.
Biol.
-
Plant
33:180
-
183.
Kumada Y., H. Anzai, E. Takano, T. Murakami, O. Hara, R. Itoh, S. Im
a, A. Satoh and K.
Nagaoka (1988) The bialaphos resistance gene (
bar
) plays a role in both self
-
defense
and bialaphos biosynthesis in
Streptomyces hygroscopicus
.
The Journal of Antibiotics.
Vol XLI, No. 12. Pp 1838
-
1845.
Leung H., Pat Loomis, and Martin L
. Pall.
"
Transformation of
Magnaporthe grisea
to
phosphinothricin resistance using the
bar
gene from
Streptomyces hygroscopicus."
Department of Plant Pathology, Washington State University, Pullman, WA 99164
-
6430.
<
http://www.fgsc.net/fgn42/leung.html
> Accessed: [10/31/2011 2:12:16 PM].
Schwartz D, S. Berger, E. Heinzelmann, K. Muschko, K. Welzel, and W. Wohlleben (2004)
Biosynthetic Gene Cluster of the Herbicide Phosphinothricin Tripeptide from
Streptomy
ces viridochromogenes
Tu494.
Applied And Environmental Microbiology
70:12
Pp. 7093
-
7102.
Schwartz D, N. Grammel, E. Heinzelmann, U. Keller and W. Wohlleben (2005) Phosphinothricin
Tripeptide Synthetases in
Streptomyces viridochromogenes
Tu ¨494
.
Antimicrobia
l Agents
And Chemotherapy
, 49:11, Pp. 4598
-
4607.
Thompson CJ
, N.R
.
Mova
a
, R
.
Tizard,
R
.
Crameri,
J.E.
Davies
,
Marc Lauwereys
and Johan
Botterman
(1987)
Characterization of the herbicide
-
resistance gene
bar
from
Streptomyces hygroscopicus
.
The EMBO Journal
6
:
9 pp.2519
-
2523.