
|
Advisory Note For Hospitals |
 |

Hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) are on the rise despite efforts to decrease them. HAIs cause an estimated 100,000 deaths annually and account for up to $45 billion in health-care costs. In USA only about 2 million patients get affected with HAI out of which around 90,000 die. HAIs are a significant cause of morbidity and mortality. At any given time, about 1 in every 20 inpatients has an infection related to hospital care. These infections cost the U.S. health care system billions of dollars each year and lead to the loss of thousands of lives. In addition, HAIs can have devastating emotional, financial and medical consequences. It has been estimated that an incidence of hospital acquired infection increases the hospital care cost of a patient by $10,375 (USD) and it increases the length of stay by 3.30 days, and that a disproportionately higher portion of the cost is attributable to Medicare. Even in India average cost for treatment of HAI is Rs. 704,175±57,804/-.Adding fuel to the fire, bacteria increasingly are becoming resistant to last-resort drugs. 
Antibiotics has been a golden bullet in the treatment of various diseases caused by microbial infections so far but not anymore, we have entered a post antimicrobial era. Misuse and overuse of antibiotics over the years have rendered them powerless to fight against infections. A "superbug"-deadly, antibiotic-resistant bacterium are the first outcome of over exposure and frequent use of antibiotics, gene mutations and gene shuffling have resulted in the formation of new proteins that can counteract the antibiotic's mechanism of action. A new strain of the drug-resistant "superbug" MRSA has been found in British cows, and it appears to be spreading to people, reports the BBC.The study published in the journal Lancet Infectious Diseases, warned that a gene - named New Delhi-Metallo -1 (NDM-1) had been found in bacterial infections, which made them resistant to almost all antibiotics, with "an alarming potential to spread". Of 29 cases in Britain examined in the study, at least 20 of the patients had visited India and Pakistan in the last year, and most had undergone surgery while they were abroad. People in three states were fallen prey to a new breed of superbugs, bacteria carrying a gene that makes them impervious to virtually any antibiotic. All three patients had recently received medical treatment in India, where the gene was first discovered, and has become widespread, the AP reports. 
A hospital-acquired infection, development is favoured by a hospital environment, such as one acquired by a patient during a hospital visit or one developing among hospital staff. Such infections include fungal and bacterial infections and are aggravated by the reduced resistance of individual patients, specially the individuals with weak immune system such as people having:
Microorganisms involved in most nosocomial infections:

Under a condition where a superbug/multidrug resistant microbe entered the host having a compromised immune response, the results will be sure shot devastating on both financial and emotional grounds. Thus hospitals are required to have a high level of sterility throughout their premises as they are the epitome of hygiene and sanitation. Despite this unified concern, the data from individual countries shows that infectious disease priorities do vary widely across the world. For example in India the top three concerns are illnesses that cause seasonal colds (47.3 percent), skin infections (37.1 percent) and seasonal flu (31.9 percent). 
Our product ATZ-Touch will form an impermeable cover upon application, which will remain on the surface for long duration. Since ATZ-Touch is not consumed during the mode of action it protects the surface from microbes for long duration of time. ATZ-Touch is not involved in chemical kill but mechanical there is no chance of development of superbugs against this technology, because of this property ATZ-Touch is effective against almost every microbe. ATZ-Touch is even effective against multiple drug resistant microbes such as MRSA, NDM-1, etc. The protective covering through ATZ-Touch not only makes things sterile but will also avoid cross-contamination, helping in reducing the nosocomial infections.Click on the link for more information about ATZ-Touch and for FAQs. 
Contaminated linen is generated by hospitals, care homes, nursing homes and similar facilities, as well as in the home care setting; anywhere that care of the sick and infirm is undertaken. The nature of laundry soiling depends on the source, and at the most extreme levels, e.g. in hospital and nursing home environments, is likely to include blood, wound exudates, sputum, saliva, sweat and urine, as well as vomit and faeces. It is also important to recognise that bloodstained body wastes such as urine may also serve as a potential source of infection. Investigators at Denver Health performed a randomized, controlled trial to assess the degree of bacterial colonization and contamination by MRSA on work clothes. The main findings of the study were: No difference in overall bacterial counts between the white coats and the uniforms No difference in MRSA contamination (16% for white coats vs. 20% for uniforms). Current recommended treatments to ensure cleaning and disinfection of used (soiled and foul) linen
Current recommended treatment to ensure disinfection of heat labile linen
List of the microorganisms surviving on hospital textiles after laundering

ATZ-FABrich is a must to have product for hospital industry, when mixed with the laundry during washing ATZ-FABrich forms a protective layer onto the cloth and protect it from microbial contamination for next 40 washes. This active shield mechanically kills the invading microbe and thus keeps it sterile, ATZ-FABrich makes cloth safe for both patient and the service provider. 
Surgical room are required to be sterile at all the time during and post a surgical operation. Single contamination can easily put the reputation of the organisation and the life of the patient at stake. According to the study the patients' charts/files in the ICU were usually contaminated with pathogenic and potentially pathogenic bacteria,several bacteria had been isolated from the charts, including multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, and Klebsiella pneumoniae, same bacteria were isolated from patients. Contaminated charts can serve as a source for cross-infection. A person can easily contaminate the equipment in the surrounding or where ever he/she may touch like patient's body. Conventional methods that use alcohol based disinfectants and sanitisers are not effective against many microbial stains. And most of the chemicals have led to the microbial adaptation to form super bugs, hard to counteract. Examples of Medical Devices which require high level of sterility but hard to make sterile.

Multiple studies have demonstrated that portable healthcare equipment, such as stethoscopes, tourniquets, sphygmomanometer cuffs, electronic thermometer handles, otoscopes and pagers also become contaminated, like hands, and can serve as a potential vector for antibiotic-resistant pathogens to patients, either via direct contact or by contamination of clinician's hands.Click on the link for more information about ATZ-Mobi friend 
Our product ATZ-Touch can easily overcome
these problems, since during application it forms a fog in the section
where it is applied, this leads to a cover on each and every object in the
surrounding. Thus covering every part of the equipment, objects, which are
hard to sterilize.ATZ-Touch will not only sterilize the object but it will
protect it for next 30 days from any kind of microbial contamination. Thus
ATZ-Touch will make and keep your surrounding sterile for 30 days round
the clock. 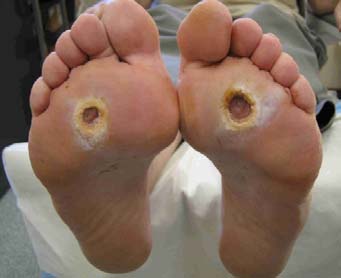
Research have mentioned that shoe can be a heaven for microbial growth, inside of shoe is a dark and warm place, sweat glands in our foot provides the required moisture for microbes to thrive in, smell from the socks are symptoms of bacterial growth and one should be serious about their hygiene if they can smell it.Since there has been an increase in the number of individuals with diabetes, there has been a huge increase in the number of individuals suffering from diabetic foot, a medical condition where sores are developed due to limited peripheral neuropathy, vascular insufficiency and diminished neutrophil function.Patient with diabetic foot have to take special care of their foot as negligence could lead to amputation of the organ. Diabetic foot patients have to examine their footon frequent basis, always keep it dry, and wear clean and soft socks, to keep their foot under good and healthy condition. Despite of these efforts there has been cases where the individual got infected and the condition became acute.More than 60 percent of nontraumatic lower-limb amputations occur in people with diabetes. However these conditions can be avoided with the help of our product ATZ-Dew which will protect the foot from any invading microbe and will keep protecting for next 24 hours.ATZ-FABrich can be used to wash the socks and other garments to protect the foot and the individual for longer duration. ATZ-Touch can be applied inside and outside the shoe, this will avoid any growth of the microbe in the shoe. Thus this combination will provide the individual a sure shot protection against and will help in quick recovery of the wound. Mobile phones have been proved to be a great source of contamination. They are one of the most of frequently used electronic gadgets by everyone in the present world. Even hospital staff do carry a phone with them, there is a high probability of transmitting the disease among others through the phone, or there could be a chance that a staff could carry a pathogenic or life threating microbe back home to their loved ones. Our product ATZ-Mobi friend provides the protective cover to your mobile and other electronic items and make sure that neither you nor your loved ones come in contact with any microbe through your phone, once applied it will keep your phone sterile for next 30 days and will not allow growth of any microbe.

Canteen plays a great role in filling the appetite of hospital staff and visitors. If not managed properly a canteen can be huge source of contamination.There has been various incidences which have forced closer of the canteen and heavy penalty to the owner, in a recent event food safety officials ordered the closure of the canteen on the campus of the Peroorkada Government Hospital on charges of cooking and serving food under unhygienic conditions, and for unhealthy maintenance of surroundings. Hospitals being a hub for eliminating various microbes, sometime serves as a reservoir of microbe. Any unhygienic practice in cafeteria can lead to a huge number of HAIs and other difficult to treat disease caused by superbugs. Our product ATZ-Touch can be used to protect everything in kitchen environment including utensils, preparation desk, cutting and chopping tools, food containers, even walls and ceiling, ATZ-Touch will form a protective layer on the device its applied and will protect it from microbes for 30days during which microbial load will not increase and thus will eliminate the risk of contamination. Our product ATZ-Dew will provide anti-microbial protection to the hands of each and every employee working in the kitchen. By the application of this product, the need of washing hands every hour or so will be eliminated. Washing chef's uniform and other clothing with ATZ-FABrich will provide another protection from the microbes and will avoid any cross contamination. |
 Gloves that are being used by the staff
provides protection only to the person wearing them, but they readily
participate in the cross contamination of microbes. Clinician's and other
staff members should use
Gloves that are being used by the staff
provides protection only to the person wearing them, but they readily
participate in the cross contamination of microbes. Clinician's and other
staff members should use